Last year my daughter had a urine organic acid test done. That test shows many different markers for yeast, bacteria, vitamins, ketones, and mitochondria. Out of all the markers every single one was out of range except one. That means my daughter’s mitochondria situation was pretty grim. She was pretty sick at the time.
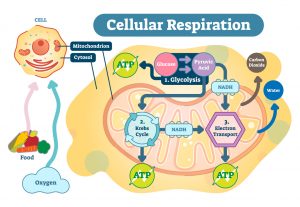
The mitochondria are the energy powerhouses of every cell of the body. They convert food and oxygen into energy called ATP. Mitochondria help detox poisons like pesticides, toxins in food, pollution in the air etc. metabolism creates a leftover substance called ash or smoke and soot which is also called oxidative stress this can injure the mitochondria. Other things that can cause oxidative stress are medications, heavy metals, chemicals, and pesticides. Oxidation in nature is like when iron rusts in the presence of oxygen and moisture. Another example is when you cut an apple and it starts to turn brown that is oxidation. If you put lemon juice and antioxidant on it, it will keep it a lighter color longer.
There are a few organs that use more energy than other parts of the body. The brain uses 22-25% of total energy made in the body per day. the liver uses 21%, muscles 22%, the heart 95 and the rest of the body 16% which include the bowel, nerves, and immune function. The cells in those organs and body parts have a higher amount of mitochondria.
The mitochondria when working their best help reduce fatigue, pain, and brain thinking problems. You actually inherit your mitochondria from your mother genetically.
Jess and I for a brief time when I was making flaxseed protein bites were eating carnitine which is an amino acid that helps get nutrients from fats into the cells. Those nutrients from fats like MCT oil from coconut oil can be used as energy for the brain and body to use instead of glucose which is the form of energy that is most used.
Other nutrients the body needs to utilize fatty acids for the production of energy are carnitine, riboflavin, niacin, and COQ10. Deficiencies of folate and other B vitamins will impair mitochondria. A few other important nutrients for the mitochondria are vitamin C, glutathione, and alpha lipoic acid all of which are important for detox and lowering oxidative stress or free radicals in the body.
So Jessica had possible high oxidative stress from heavy metals, medications that I was taking and she was getting through the breast milk, other chemicals and possibly chemicals from plastics. She was also low in B2 and B12. I had been taking what I thought was a safe amount of fiorcet for migraine headaches. I had called the infant risk hotline where they have trained knowledgeable nurses to ask questions of at https://www.infantrisk.com/ to make sure the amount of medication I was taking was safe for babies and the amount I was taking they said was safe but it did cause a glutathione deficiency and likely other deficiencies too.
The bottom line with mitochondria I think is best said from Dr. Terry Wahl’s in her book The Wahl’s Protocol, “When your mitochondria aren’t powering your body correctly, everything begins to malfunction in a negative spiraling chain reaction that eventually relates to cell aging, organ dysfunction, and chronic disease. Science increasingly shows that mitochondrial strain is at the root of most of the chronic diseases afflicting modern society.” Pg. 34
A few things I recently learned about helping to boost mitochondria function are a) a mild ketogenic diet which lowers carbs, eliminates grains basically, and intends to use fats for energy instead of glucose b) calorie restriction, intermittent fasting, intellectual stimulation, and meditation. (Mito food plan comprehensive guide)
In addition the basic diet and supplements above there are a few foods especially good for the mitochondria. I thought it was really interesting learning about these foods in my functional medicine health coaching program because I was eating most of these foods on a regular basis and even in the way they were recommended. I truly do feel the best when I am eating this way. I’ll list out these foods and just a bit about what they contain and why they are so important:
1. Almonds – have mono unsaturated fat, vitamin E, glutathione. They also contain calcium and magnesium. It is recommended to only eat about a scant handful so as not to overeat these which is so easy to do at least for me.
2. Avocado – these have fiber, folate, potassium, vitamin E and glutathione.
3. Blueberries – studies from Tufts university show that proanthocyanidins in blueberries are responsible for learning and memory but they can change cell signaling patterns and oxidative patterns in neurons. I ate a lot of these instinctively when I had to have multiple X-rays when I was pregnant, this fruit is such a powerhouse.
4. Broccoli – and the broccoli family like cabbage, cauliflower, and kale contain nutrients that help the body make glutathione the master antioxidant.
5. Coconut oil – the medium chain triglycerides in coconut oil seem to used by the brain very readily as an energy source. It doesn’t require the same mechanism of digestion which lowers energy expenditure in processing through the body. Coconut oil is also antifungal, antimicrobial, and antiviral.
6. Green tea – contains catechins are protective of the mitochondria.
7. Olive oil – polyphenols which cloudy or unfiltered olive oil may have.
8. Pomegranate – protective polyphenols.
9. Salmon – rich in omega 3’s.
10. Sea weed – high in minerals the mitochondria require to function
11. Spinach – all greens, the darker color is better because it is richer in chlorophyll, carotenoids, and anti-inflammatory compounds.